Bland-Altman分析是验证设计用于测量相同参数的两种方法之间的一致性或不一致程度的过程。 方法之间的高相关性表明在数据分析中选择了足够好的样品。 在SAS中,我们通过计算变量值的平均值,上限和下限来创建一个Bland-Altman图。 然后我们使用PROC SGPLOT创建Bland-Altman图。
在SAS中应用PROC SGPLOT的基本语法是:
PROC SGPLOT DATA = dataset; SCATTER X=variable Y=Variable; REFLINE value;
以下是使用的参数的描述:
在下面的例子中,我们取两个名为new和old的方法生成的两个实验的结果。 我们计算变量值的差异以及相同观察值的变量的平均值。 我们还计算要在计算的上限和下限中使用的标准偏差值。
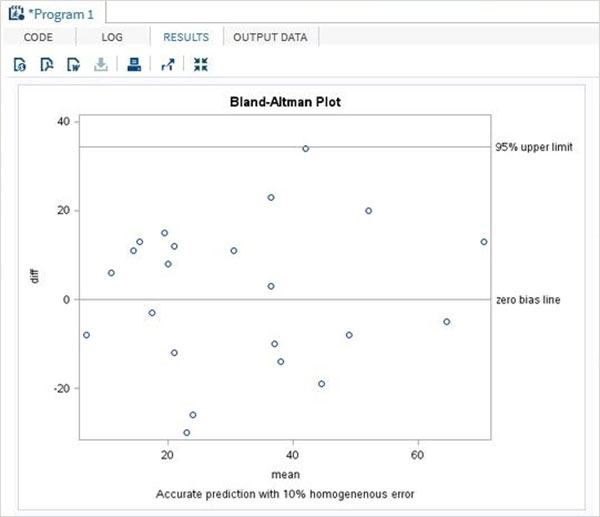
结果显示Bland-Altman图为散点图。
data mydata;
input new old;
datalines;
31 45
27 12
11 37
36 25
14 8
27 15
3 11
62 42
38 35
20 9
35 54
62 67
48 25
77 64
45 53
32 42
16 19
15 27
22 9
8 38
24 16
59 25
;
data diffs ;
set mydata ;
/* calculate the difference */
diff=new-old ;
/* calculate the average */
mean=(new+old)/2 ;
run ;
proc print data=diffs;
run;
proc sql noprint ;
select mean(diff)-2*std(diff), mean(diff)+2*std(diff)
into :lower, :upper
from diffs ;
quit;
proc sgplot data=diffs ;
scatter x=mean y=diff;
refline 0 &upper &lower / LABEL = ("zero bias line" "95% upper limit" "95%
lower limit") ;
TITLE 'Bland-Altman Plot';
footnote 'Accurate prediction with 10% homogeneous error';
run ;
quit ;
当执行上面的代码中,我们得到以下结果:
在上述程序的增强模型中,我们得到95%的置信水平曲线拟合。
proc sgplot data=diffs ;
reg x = new y = diff/clm clmtransparency= .5;
needle x= new y=diff/baseline=0;
refline 0 / LABEL = ('No diff line');
TITLE 'Enhanced Bland-Altman Plot';
footnote 'Accurate prediction with 10% homogeneous error';
run ;
quit ;
当执行上面的代码中,我们得到以下结果:
